Different types of uterine fibroids require different types of treatment
The treatment strategy for patients with fibroids varies depends upon the type of uterine fibroid, size and location as well as multiple other patient-specific factors.
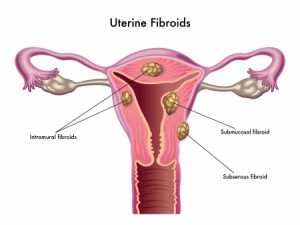
Submucous fibroids grow within the inner cavity of the uterine and usually cause abnormal menstrual bleeding. The bleeding can occur at the time of normal menstrual bleeding or it can occur at other times during the cycle. It may also be so heavy that it leads to anemia. These benign tumors require removal even if a patient is not attempting pregnancy. Most of these fibroids can be removed hysteroscopically if the majority of the fibroid is within the cavity of the uterus.
This involves placing a slim telescope through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. They are not thought to play a major role in infertility, but they may be removed if they are causing you other symptoms, such as pain or pressure on surrounding organs like your bladder or intestine.
Intramural fibroids grow within the wall of the uterus. If they are larger than3-4 cm, they may be removed either by a laparoscopy or laparotomy. A laparoscopy is an outpatient procedure during which a slim telescope is passed through the belly button into the abdomen. Additional surgical instruments are passed through 1-2 other small incisions (< 1cm) made just above the pubic bone. Using these instruments, your physician can remove the fibroids and repair the uterus so that it will retain its normal function.
Other uterine abnormalities include fibroids that are attached to the outside of the uterus (subserosal fibroids).
The further the fibroid is away from the endometrial cavity the less it becomes a factor in regard to fertility and/or carrying a pregnancy.











